Two projects from the INHS PACE Lab were among the 21 projects funded nationally by the 2021 U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s Competitive State Wildlife Grant (C-SWG) program.
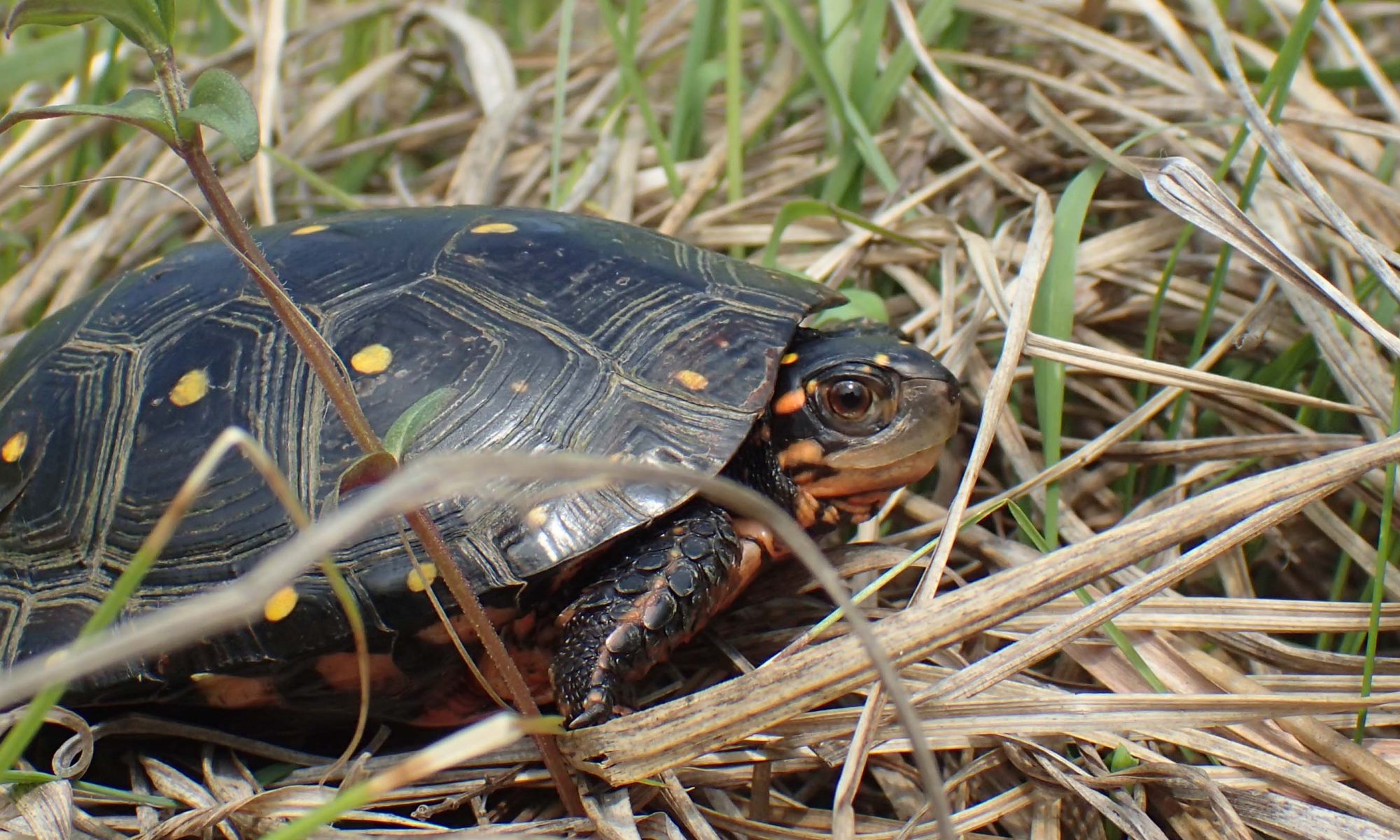
 The first cooperative project is with the Iowa and Illinois Department of Natural Resources, allocated at $499,797 for the joint project titled “Blanding’s Turtle Conservation in Iowa and Illinois, 2022 through 2024”. The project team from the Illinois Natural History Survey (INHS) and National Great Rivers Research and Education Center (NGREEC) comprises Ethan J. Kessler, Michael J. Dreslik, Andrew R. Kuhns, and John A. Crawford. The team was awarded $249,449 for their portion of the project, “Population Assessment and Space Use in a Kankakee Sands Region Blanding’s Turtle Population.” While much work has been done on Blanding’s Turtle populations in the Chicagoland region, this project focuses on lesser-known populations in the Kankakee Sands Conservation Opportunity Area.
The first cooperative project is with the Iowa and Illinois Department of Natural Resources, allocated at $499,797 for the joint project titled “Blanding’s Turtle Conservation in Iowa and Illinois, 2022 through 2024”. The project team from the Illinois Natural History Survey (INHS) and National Great Rivers Research and Education Center (NGREEC) comprises Ethan J. Kessler, Michael J. Dreslik, Andrew R. Kuhns, and John A. Crawford. The team was awarded $249,449 for their portion of the project, “Population Assessment and Space Use in a Kankakee Sands Region Blanding’s Turtle Population.” While much work has been done on Blanding’s Turtle populations in the Chicagoland region, this project focuses on lesser-known populations in the Kankakee Sands Conservation Opportunity Area.
The grant will facilitate an intensive capture-mark-recapture study to determine population size and begin to collect demographic data. A subset of turtles will be tracked using radio telemetry and GPS trackers to monitor survival and determine space and habitat use. The data is necessary to determine the amount and extent of suitable habitat available on the landscape and address causes of mortality for this population. The work will build on previous research on Blanding’s Turtles in Illinois and further inform conservation planning.
 The second cooperative project is with the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources allocated at $247,892 for the joint project titled, “Regional Assessment of Widespread Mussel Declines: a Multistep Approach to Examine Potential Causes.” The project team from the INHS comprises Sarah A. Douglass and Alison P. Stodola while INHS alum Bernard Sietman will lead Minnesota’s portion. The INHS team was awarded $113,364 for their portion of the project. Freshwater mussels, an ecologically important component of river ecosystems, are experiencing widespread declines. With the award, Douglass and Stodola will investigate potential causes for these declines with the goal of informing conservation guidelines and recovery planning. Additionally, this study is an expansion of a largescale, cooperative project spearheaded by Dr. Wendell Haag, US Forest Service Research Fisheries Biologist, and American Rivers to examine causes of freshwater mussel declines across North America.
The second cooperative project is with the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources allocated at $247,892 for the joint project titled, “Regional Assessment of Widespread Mussel Declines: a Multistep Approach to Examine Potential Causes.” The project team from the INHS comprises Sarah A. Douglass and Alison P. Stodola while INHS alum Bernard Sietman will lead Minnesota’s portion. The INHS team was awarded $113,364 for their portion of the project. Freshwater mussels, an ecologically important component of river ecosystems, are experiencing widespread declines. With the award, Douglass and Stodola will investigate potential causes for these declines with the goal of informing conservation guidelines and recovery planning. Additionally, this study is an expansion of a largescale, cooperative project spearheaded by Dr. Wendell Haag, US Forest Service Research Fisheries Biologist, and American Rivers to examine causes of freshwater mussel declines across North America.
Researchers will assess pairs of rivers with similar historic mussel assemblages, comparing a river with relatively intact mussel assemblages and a river with a degraded assemblage. They will develop health metrics and assess habitat characteristics to identify potential causal factors of decline. Juvenile mussels will be propagated and used to assess health in response to potential causes of decline. Another part of the project will use eDNA and targeted sampling to update knowledge of Salamander Mussel populations in Illinois and Minnesota. The research will build on a pilot project previously undertaken by Douglass to use eDNA to detect the critically imperiled species and its host, the Mudpuppy salamander.
In granting these awards, USFWS recognizes the necessity of these two projects to further the goals of the Illinois Wildlife Action Plan to conserve imperiled species and their habitats.
 The Urban Biotic Assessment Program was awarded $6,226,400 to continue providing technical assistance to the Illinois Tollway Environmental team.
The Urban Biotic Assessment Program was awarded $6,226,400 to continue providing technical assistance to the Illinois Tollway Environmental team.