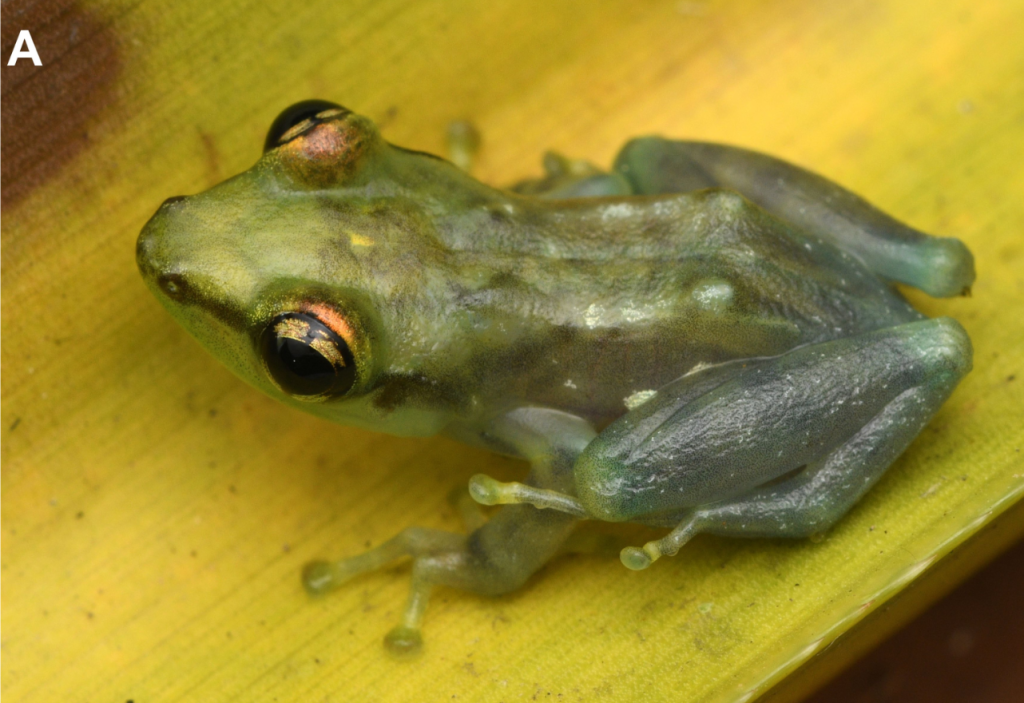
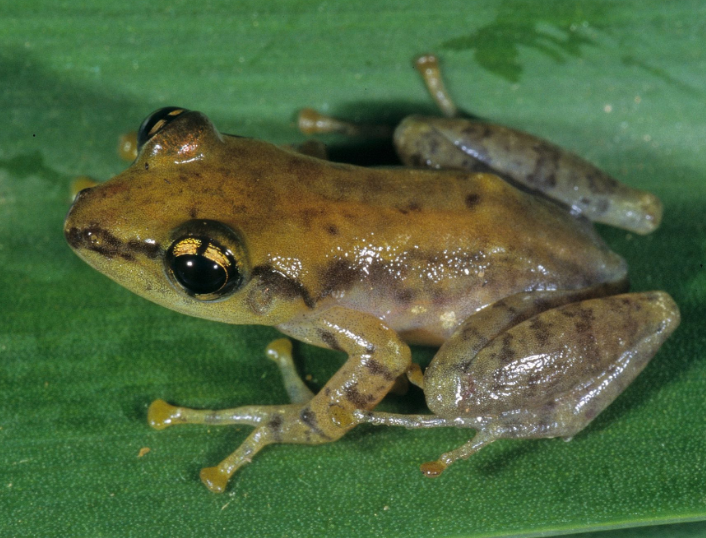
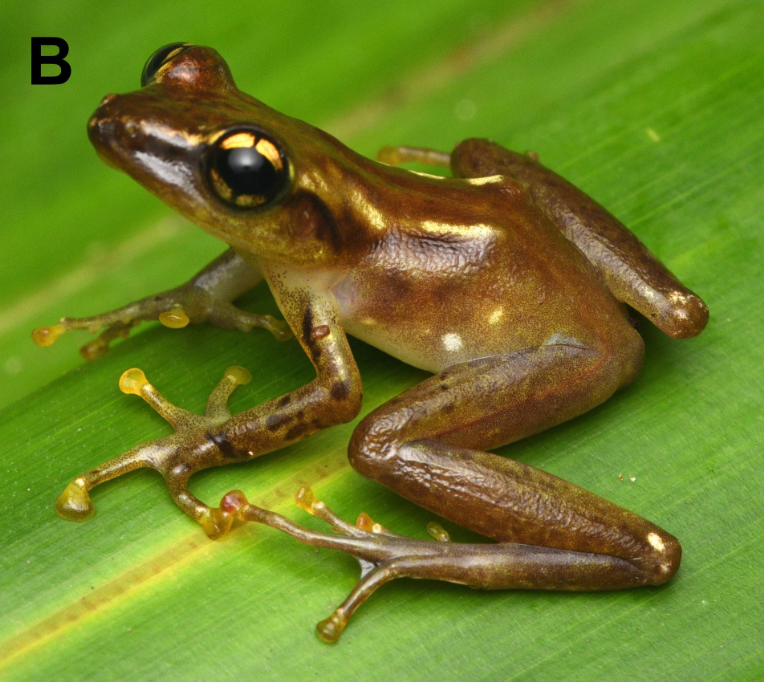
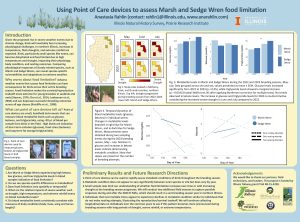
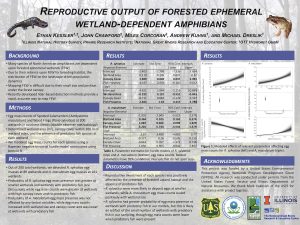
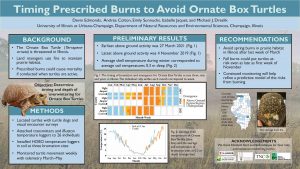
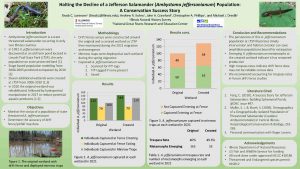
Three new species of frogs from Madagascar were described in a paper co-authored by PACE Lab PhD candidate Devin Edmonds, led by researchers at Zoological Institute at Technische Universitat Braunschweig.
The group of frogs, Genus Guibemantis, subgenus Pandanusicola, spend their lives in the Pandanus (screw-pine) trees, which are common in the Andasibe area of Madagascar. They live and reproduce in water that pools in the leaves of the trees. While surveying the trees, the researches observed frogs that did not look like any known species Genetic testing revealed 4 new species for the region, 3 of which were new to science.
Read an article in the Miami Herald
Read the full paper at
Hugh Gabriel, Laila-Denise Rothe, Jörn Köhler, Sandratra Rakotomanga, Devin Edmonds, Pedro Galán, Frank Glaw, Richard M. Lehtinen, Andolalao Rakotoarison and Miguel Vences. 2024. Unexpected Diversity and Co-occurrence of phytotelmic Frogs (Guibemantis) around Andasibe, one of the most intensively surveyed Amphibian Hotspots of Madagascar, and Descriptions of Three New Species. Zootaxa. 5397(4); 451-485. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.5397.4.1